Modeling of Industrial Printing and Nano-Jetting Spray Delivery
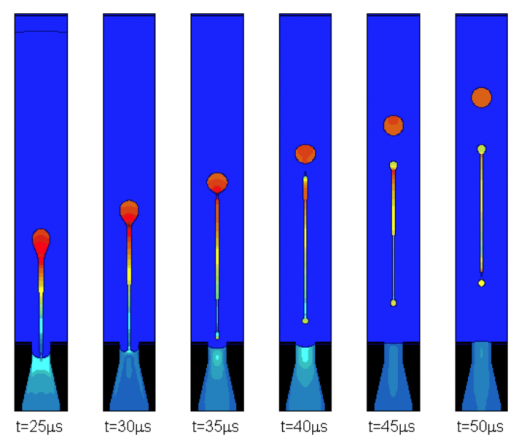
We built a computational environment to model two-phase microjetting in manufacturing and industrial devices. The code is a fully three-dimensional computational model simulating both Newtonian and Oldroyd-B viscoelastic fluids in two-phase immiscible incompressible flows with surface tension and both viscosity/density jumps across interfaces separating viscoelastic fluid from air. This model includes a contact model for air/wall/fluid interactions, and incorporates complex geometries. The model has been used to predict performance characteristics of inkjet industrial printers for use in manufacturing integrated circuits and micro-jetting devices.
About Berkeley Lab
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab’s facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.









