Cosmic Coding
Using advanced numerical simulations, Berkeley Lab and Argonne computational cosmologists help astronomers turn observation into insight.
Data Processing Pipeline Transforms Planck Mission
Reijo Keskitalo, a member of Computational Cosmology Center, was awarded NASA’s Exceptional Public Achievement Medal for “developing novel tools and approaches for maximizing NASA’s understanding of t…
Self-Supervised Learning for Sky Surveys
Sky surveys are the largest data generators in astronomy, making automated tools for extracting meaningful scientific information an absolute necessity.
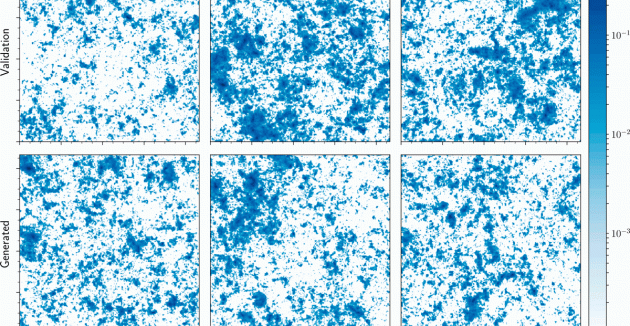
CosmoGAN: Using Neural Nets to Study Dark Matter
“We were looking for two things: to be accurate and to be fast,” said co-author Zarija Lukić, a research scientist in the Computational Cosmology Center at Berkeley Lab. “GANs offer hope of being near…

Modeling 3D Map of Adolescent Universe
Using extremely faint light from galaxies 10.8 billion light years away, scientists including researchers from CRD's Computational Cosmology Center have created one of the most complete, three-dimensi…
In recent years astrophysics has undergone a renaissance, transforming from a data-starved to data-driven science. A new generation of experiments are gathering data sets so massive that their analysis will require the use of leading-edge, high-performance computing resources. Furthermore, interpreting this data requires powerful modeling using supercomputer numerical simulations and state-of-the-art statistical and machine learning methods.
As a multi-disciplinary center, C3 is bringing together astrophysicists and computational scientists whose goals are to develop the methods, tools, and technologies to meet the scientific challenges of modern cosmology. Our current activities include:
- Developing the tools needed to manage the data from the ongoing and future Cosmic Microwave Background missions, like the CMB-S4 and Simons Observatory.
- Building astrophysical transients discovery pipelines, used for finding Supernovae type Ia and other transients.
- Simulating the large-scale structure of the universe using Nyx code, focusing on the intergalactic medium and Lyman alpha forest.
- Developing and deploying AI and machine learning technologies to analyze large data sets, to build surrogate models augmenting expensive numerical simulations, and to improve the process of scientific inference.
- Computing support for large sky surveys, like DESI and the Dark Energy Science Collaboration of the Vera Rubin Observatory.
Center lead: Zarija Lukić



























