
Exabiome Project
Exabiome project is developing exascale computing tools to solve previously infeasible science problems in genomic analysis.
RAPIDS2
RAPIDS2 SciDAC5 Institute assists Office of Science application teams in overcoming computer science, data, and AI challenges in using DOE supercomputing resources to achieve scientific breakthroughs.

ENDURABLE
The ENDURABLE project aims to provide the scientific community with tools to aggregate data robustly and train our deep learning models.

Scalable Graph Learning for Scientific Discovery
Graph representation learning is transforming scientific domains from structural biology to particle physics, transportation, and beyond.
SciDAC-5: DECODE
Data-driven Exascale Control of Optically Driven Excitations in Chemical and Material Systems (DECODE) combines exascale and non-traditional machine learning for advances in optical systems.
The Performance and Algorithms Research Group focuses on the research and development of technologies and algorithms that enhance the performance, scalability, and energy efficiency of applications running on the Department of Energy's multicore-, manycore-, and accelerator-based supercomputers. Moreover, we develop performance models to understand the inherent bottlenecks in today's systems as well as predict the performance and bottlenecks of tomorrow's exascale systems. To that end, we have formed strong research collaborations with computer science, computer architecture, applied math, and application research teams.
Group Leader: Lenny Oliker
EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNITIES
The Performance and Algorithms Research Group has opportunities to join our team and work closely with leading researchers to enable scientific breakthroughs on the world’s most power supercomputers. Our group consistently publishes in prestigious journals and conferences, and engages in exciting collaborations across a broad range of emerging computer science challenges.
- Sparse Computations Postdoctoral Scholar (97038)
Research
ExaBiome
Roofline Performance Model
RAPIDS2
Exagraph
Scalable Graph Learning for Scientific Discovery
Parallel Primitives for Randomized Algorithms on Sparse Data
ENDURABLE
SciDAC-5 Institute
SciDAC-5 SAP: Correlated Electrons in QM
SciDAC-5 SAP: DECODE
ECP PROTEAS-TUNE
Performance Analysis of AI Hardware and Software
High Performance Geometric Multigrid
CSPACER
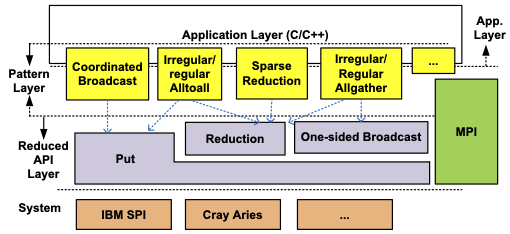 CSPACER is a lightweight communication runtime for application-specific optimized communication patterns.
CSPACER is a lightweight communication runtime for application-specific optimized communication patterns.
































