News Center
Carbon Dioxide Catchers
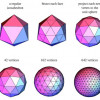
CRD's Maciej Haranczyk and colleagues have developed a computational tool that can help researchers sort through vast databases of porous materials to identify promising carbon capture candidates—and at record speeds. They call it Zeo++.
Read More »
John Shalf's Paper is Among the Best in History of HPDC Conference
“The Cactus Code: A Problem Solving Environment for the Grid,” a paper co-authored by John Shalf of the Computational Research Division, has been selected as one of the top papers in the 20 years of publications from HPDC, the International ACM Symposium on High-Performance Parallel and Distributed Computing (HPDC). Read More »
Berkeley Lab Mathematicians Win Cozzarelli Prize
James Sethian and Robert Saye, mathematicians who both hold joint appointments with the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) and the University of California (UC) Berkeley, have won the 2011 Cozzarelli Prize for the best scientific paper in the category of Engineering and Applied Sciences. Read More »
Breaking Ground on the Computational Research and Theory Facility
Energy Secretary Steven Chu, along with Berkeley Lab and UC leaders, broke ground on the Lab’s Computational Research and Theory (CRT) facility, Wednesday, Feb. 1. The CRT will be at the forefront of high-performance supercomputing research and be DOE’s most efficient facility of its kind. Read More »
Billions of Genes and Counting!
Developed by CRD's Biological Data Management & Technology Center, the IMG/M data management system, which supports the analysis of microbial communities sequenced by the Joint Genome Institute, crossed the boundry of 1 billion genes recorded in the system—more than any other similar system in the world. Read More »
Inspiring Careers in Science Research
In an effort to expose high school students to careers in science research, the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s (Berkeley Lab) Computing Sciences Diversity Outreach Program partnered with San Francisco’s Lowell High School research program. Read More »
Closest Type Ia Supernova in Decades Solves a Cosmic Mystery
Even as the "supernova of a generation" came into view in backyards across the northern hemisphere last August, physicists and astronomers who had caught its earliest moments were developing a surprising and much clearer picture of what happens during a titanic Type Ia explosion. Now they have announced the closest, most detailed look ever at one of the universe’s brightest “standard candles,” the celestial mileposts that led to the discovery of dark energy. Read More »
A Better Way to ID Extreme Weather Events in Climate Models
A team of researchers that includes Berkeley Lab scientists are using state-of-the-art methods in data mining and high-performance computing to quantify extreme weather phenomena in the very large datasets generated by today’s climate models. Their work will help scientists predict how climate change impact the frequency of extreme weather events. Read More »
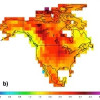
Today’s Severe Drought, Tomorrow’s Normal
While the worst drought since the Dust Bowl of the 1930s grips Oklahoma and Texas, scientists are warning that what we consider severe drought conditions in North America today may be normal for the continent by the mid-21st century, due to a warming planet. Read More »
Supercomputers Take a Cue from Microwave Ovens
To build the break-through supercomputers that climate researchers need to model clouds, scientists are taking a cue from consumer electronics where everything from chips to batteries to software is optimized to the device’s application. Read More »
Computing Tools Speed Search for New Porous Materials
A team of Berkeley Lab and the UC Berkeley researchers are speeding the search for new porous materials through computation. Read More »
Experimental Mathematics: Computing Power Leads to Insights
Modern computer technology has vastly expanded our ability to discover new mathematical results. Read More »
Distant Supernovae Reveal 10 Billion Year-old Secret
Type Ia supernova were five times more frequent in the early universe than today, found astronomers who exposed the largest sample of distant supernovae ever found. Many of the 150 events are 10 billion light years distant from Earth. Read More »
Nobel Laureate a Computational Cosmology Pioneer
Winner of the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physics, Saul Perlmutter leads a research team believed to be the first to use supercomputers to analyze and validate observational data in cosmology. Read More »
Co-Designing Exascale Architectures and Algorithms for Real-World Combustion Simulations
In a five-year project recently announced by the Department of Energy, the Combustion Exascale Co-Design Center will combine the talents of combustion scientists, mathematicians, computer scientists, and hardware architects. This multidisciplinary team will work to simultaneously redesign each aspect of the combustion simulation process—from algorithms to programming models to hardware architecture—in order to create high fidelity combustion simulations that can run at the next level of supercomputing power, the exascale. Read More »
Supernova Caught in the Act
Astronomers believe they caught a nearby supernova within hours of its explosion, a rare feat made possible by a specialized survey telescope and state-of-the-art computational tools. Read More »
Vern Paxson Honored
Vern Paxson of Berkeley Lab’s Computational Research Division has been named recipient of this year’s ACM SIGCOMM Award. Read More »
CRD Researchers Receive Prizes, Present at ICIAM 2011
At the 7th International Congress on Industrial and Applied Mathematics, two of Berkeley Lab’s leading mathematicians received prizes for their research contributions. Many others gave talks, presented papers and posters, and organized technical sessions. Read More »
David L. Brown New CRD Director
David L. Brown is the new director for the Computational Research Division (CRD), as of Aug. 30. Brown comes to Berkeley Lab from LLNL. Read More »
David Leinweber Named One of Top 10 Innovators of Decade in Trading Industry
David Leinweber of the Computational Research Division has been named by Advanced Trading magazine as one of its "Top 10 Innovators of the Decade." Read More »
ICCS Members Collaborate on Award-Winning Paper
One year after Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and UC Berkeley established the International Center for Computational Science (ICCS) with partners at the University of Heidelberg in Germany and the National Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in China, the first research paper submitted by ICCS-affiliated researchers will be honored with the PRACE Award. The award, sponsored by the Partnership for Advanced Computing in Europe (PRACE), will be presented to… Read More »
Juan Meza Named New Dean of Natural Sciences at UC Merced
Juan Meza, acting director of the Computational Research Division and head of CRD’s High Performance Computing Research Department, has been named Dean of the School of Natural Sciences at UC Merced. The appointment, announced Friday, June 3, will be effective this fall. "As I was considering this position, I was truly impressed by the quality of the faculty, the commitment and diversity of UC Merced's students and the great potential to help shape the development of the newest campus in one… Read More »
Search Engine Speeds Past Competition
Berkeley Lab's open source FastBit can search massive databases 10 to 100 times faster than large commercial database software. Read More »
James Demmel Elected to National Academy of Sciences
James W. Demmel, a UCB professor and CRD researcher, is one of 72 new members elected to the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Read More »
Supercomputer Cracks "Impossible" Calculation
 David Bailey
Australian researchers have done the impossible—they’ve found the sixty-trillionth binary digit of Pi-squared! The calculation would have taken a single computer processor unit (CPU) 1,500 years to calculate, but scientists from IBM and the University of Newcastle managed to complete this work in just a few… Read More »
David Bailey
Australian researchers have done the impossible—they’ve found the sixty-trillionth binary digit of Pi-squared! The calculation would have taken a single computer processor unit (CPU) 1,500 years to calculate, but scientists from IBM and the University of Newcastle managed to complete this work in just a few… Read More »