Research
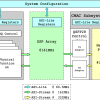
iARPA AGILE
The fundamental problem with current computer architectures is their inefficiency at operating on sparse, time-varying data that is randomly distributed across the system. The AGILE program seeks to solve this problem by developing new system-level intelligent mechanisms for accessing, moving, and storing complex data streams and structures that enable efficient data-analytic algorithms.New architectures developed under the AGILE program will be driven by representative data-intensive… Read More »
Berkeley eXtensible Processing Engine (BXPE)
With experimental facilities data production rates exponentially increasing, there is a greater need to move computation closer to the experimental source. To this end, we have developed the Berkeley eXtensible Processing Engine (BXPE) Framework, which allows experimentalists to utilize FPGAs stitched into the network pipeline to process data in real-time as it flows over the network. We provide a Python-tooling front-end to allow for development of algorithms using this framework. In this… Read More »
PARADISE++
In this project, we propose to build a post-Moore HPC (High-Performance Computing) system simulation framework to enable large scale simulations of post-Moore architectures built using emerging devices and technologies. With the HPC systems performance reaching exaflops and the transistor scaling reaching the saturation, the HPC systems to be built for post Moore era are evolving to extremely heterogeneous systems. For the Beyond Moore era, new computing, memory, interconnect and storage models… Read More »
Superconducting Race Logic Accelerators
The aim of this project is to make computation in superconducting circuits, circuits that operate around 4K temperatures and have close to zero resistance, as efficient as possible. Many approaches today try to re-use computing architectures (the design of logic gates and circuits) inspired by traditional technologies into superconducting logic. This is not efficient since superconducting circuits are different: accessing memory is very expensive but the circuit… Read More »
DFT Beyond Moore’s Law: Extreme Hardware Specialization for the Future of HPC
The project goal is to demonstrate the performance potential of purpose-built architectures as potential future for HPC applications in absence of Moore’s Law. Our approach is to reformulate the LS3DF algorithm to make it amenable to specialized hardware and to develop a custom accelerator for Density Functional Theory. The initial design/prototype will target an FPGA, and results will also be projected to an ASIC. Later, we intend to generalize our results to to broader implications for DOE… Read More »
iARPA SuperTools
The Intelligence Community (IC) is well known to be a major consumer of high performance computing, but is increasingly finding itself frustrated by limitations in overall power consumption and clock speed. The amazing successes of semiconductor technology embodied in Moore’s Law give the impression that computing power might continue on its exponential growth curve indefinitely. However there are limits of miniaturization and switching speeds imposed by physics as applied to semiconductors,… Read More »
Mobiliti
Overview Transportation systems are becoming increasingly complex with the evolution of emerging technologies, including deeper connectivity and automation, which will require more advanced control mechanisms for efficient operation (in terms of energy, mobility, and productivity).Stakeholders, including government agencies, industry, and local populations, all have an interest in efficient outcomes, yet there are few tools for developing a holistic understanding of urban… Read More »
Mota Mapper
Mota is a library that provides several heuristics for the purpose of AMR task placement. It is multi-objective in the sense that it simultaneously balances the computational load on each rank as well as the communication traffic between the boxes. We are investigating a variety of approaches to do the task placement and utilizing modeling and simulation tools to evaluate these approaches. The heuristics used for mapping include algorithms such as greedy list assignment and space-filling… Read More »
Open2C
A cache-coherent memory subsystem plays an important role in complex digital computing systems. It maintains memory consistency across on-chip caches that hide the memory latency to improve computational performance. Being managed by hardware, the cache subsystem facilitates multi-core system programming and allows developers to focus on other crucial aspects. However, due to extensive protocol-related traffic and lack of explicit data movement management, cache memory scalability becomes a big… Read More »
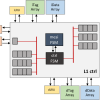
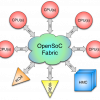
OpenSoC Fabric
Abstract Recent advancements in technology scaling have shown a trend towards greater integration with large-scale chips containing thousands of processors connected to memories and other I/O devices using non-trivial network topologies. Software simulation proves insufficient to study the tradeoffs in such complex systems due to slow execution time, whereas hardware RTL development is too time-consuming. We present OpenSoC Fabric, an on-chip network generation infrastructure which aims to… Read More »