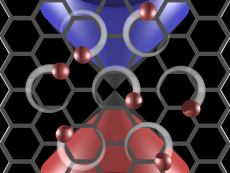
Researchers Learn to Control Graphene with Lasers
May 13, 2015
Linda Vu, +1 510 495 2402, lvu@lbl.gov
New numerical simulations by Berkeley Lab Alvarez Fellow Alexander Kemper and his colleagues at Stanford University reveal how the quantum properties of graphene can be manipulated at ultrafast timescales with femtosecond laser pulses. This work opens a new area of research, where scientists can tune and control material properties with optical laser pulses.
“What’s exciting about these simulations is that we are looking at the constituent properties of matter at their proper timescales. Electrons live at femtosecond time scales, and we can now study how their properties are affected at this timescale,” says Kemper. “By illuminating them with ultrafast lasers, we can control their conduction properties, with exciting prospects for future devices based on this concept, for example by creating ultrafast switches in a spin-based version of electronic circuits.”
The team’s work was recently published in Nature Communications.
About Berkeley Lab
Founded in 1931 on the belief that the biggest scientific challenges are best addressed by teams, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and its scientists have been recognized with 16 Nobel Prizes. Today, Berkeley Lab researchers develop sustainable energy and environmental solutions, create useful new materials, advance the frontiers of computing, and probe the mysteries of life, matter, and the universe. Scientists from around the world rely on the Lab’s facilities for their own discovery science. Berkeley Lab is a multiprogram national laboratory, managed by the University of California for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
DOE’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.